The institutional transformations of contemporary Russia are primarily aimed to principally change the life quality of population [3]. The population life quality management process provides the managing impact on the state and municipal socio-economical interrelations; however, it is not a simple task to assess the efficiency of such impact. Due to the fact that GOST ISO 9001-2011 defines the term “quality” itself as the degree of compliance of the total of inherent characteristics with the certain consumer requirements, the life quality of population will be understood as the degree of compliance of the total of inherent life-activity characteristics with the certain population requirements. The evaluation of “population life quality” by the scientists of different scientific schools [6] assumes the evaluation of the hierarchic system of the factors, criteria, and indicators that characterize comprehensively the economic development of society, material welfare level, medico-ecological and culture-spiritual well-being of population.
The institutional reforms discover the new capabilities to increase the population well-being level by means of the extra income sources [1]. From the factorial approach, the population revenues allow for not only labor payment but also returns on investment in the form of dividends, interests, property income, and the broad capabilities to use entrepreneurial skills [2]. According the Government of Russia, the revenues from sales of the production factors that are in ownership and economical processes shall significantly increase the quality of population life. In addition, the factorial model of population life quality management proposed by the author (Fig.1) [4] allows showing pictorially not only the capabilities to increase the population well-being level but also the managing system’s role in population life activity. The managing impact by the state and municipal authorities is to create a developed infrastructure, comfortable institutional environment, and special investment climate that ensure the conditions to implement easily the production factors in the economic territory [5]. Aimed to increase the quality of population life, the socio-economic system being interrelated functionally inside enables to determine the new horizons of economical, medico-ecological, and culture-spiritual development of the territory.
The factorial model of population life quality management under consideration shows the availability of three input factors which impact cannot be assessed by direct quantitative indicators but they are able to significantly change the life quality of population.
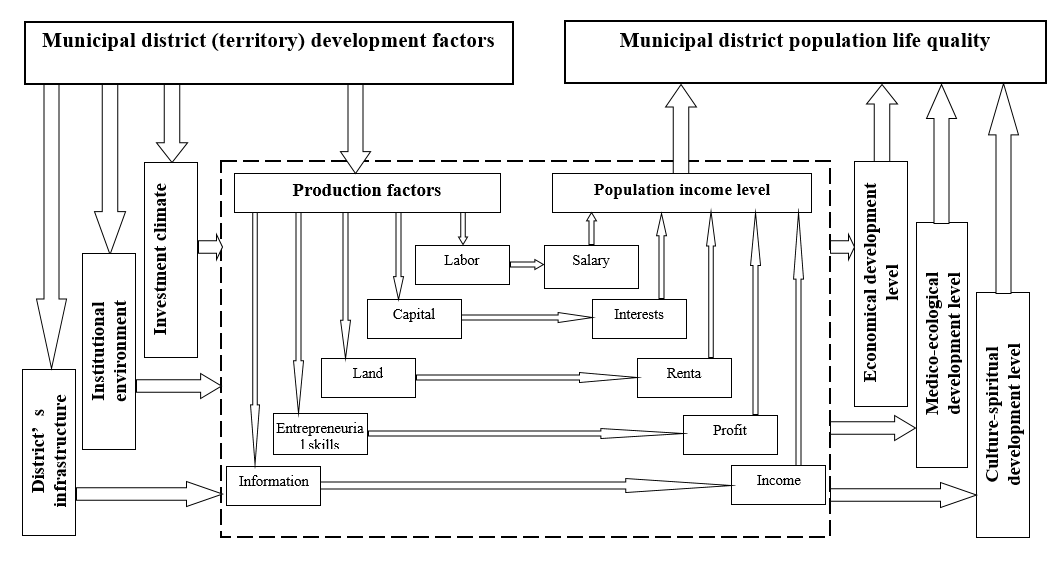
Figure 1 Factor model of population life quality management [4]
For the proposed factor model of population life quality management, the comprehensive population life quality study was conducted at the rural and municipal districts of the Nizhni Novgorod Region from 2010 to 2014, where more than 1500 persons with higher and incomplete higher education took part. The respondents were proposed to asses on a scale from one to ten their life quality components that include the general economic development, population income, spiritual well-being, and medico-ecological welfare levels. The respondents indicated their own satisfaction levels in each individual life-activity area as the degree of compliance of their requirements for the total of inherent characteristics with their life quality components. For the study, the respondents were suggested to make a prediction for 2015-2016. A portion of the study results was in the earlier works of the author [7], a complete analysis of the sociological interview results is in Table 1.
2015-2016 study was supplemented by the interview with more than 300 habitants of the Nizhni Novgorod Region of different age-grade, where assessment was “on actual basis”.
Table 1
Sociologic assessment of population life quality components for 2010-2016, score
| Components that characterize population life quality | Life quality assessment by population on a scale from one to ten | ||||||
| 2010 | 2012 | 2014 | 2015
prediction |
2015 | 2016
prediction |
2016 | |
| General economic development level | 6.6 | 6.02 | 5.76 | 4.94 | 5.04 | 5.82 | 6.78 |
| Population material well-being level | 6.36 | 5.98 | 5.86 | 4.68 | 5.08 | 5.90 | 6.41 |
| Medico-ecological service level | 5.98 | 5.94 | 5.90 | 4.92 | 5.22 | 5.40 | 5.67 |
| Culture-spiritual and patriotic development level | 6.38 | 5.74 | 5.72 | 7.12 | 7.78 | 7.46 | 7.04 |
| Average integral indicator | 6.33 | 5.92 | 5.81 | 5.42 | 5.78 | 6.15 | 6.48 |
The sociological study has shown that the predictive assessments of the life quality of population in Russia were significantly worse than the actual assessments given by the respondents on the results of the preceding years. This can be due to both the general-political situation around Russia and the negative prediction for the results of imposed sanctions. As per the prediction, in 2015, the population life quality integral indicator was expected to be reduced by 7.96% compared to 2014, and the general economic development value – by 14.26%. According to the respondents, yet more significant reduction was predicted for the population material well-being indicator group from 6.36 scores in 2010 to 4.68 scores in 2015 i.e. by 26.42%. As is seen from the table, the pessimistic predictions were not came true; the population life quality category estimations have increased by 2016 and exceeded a little the level of 2010. Figure 2 shows that three significant categories of the life quality population reduced in 2015.
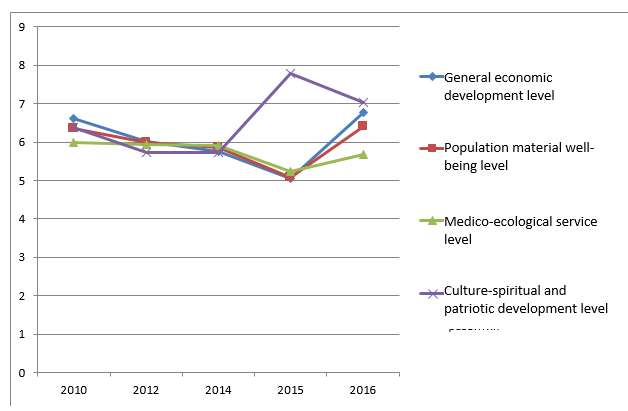
Figure 2. Sociological assessment of population life quality for 2010-2016 (actual)
Equalization of the integral indicator of population life quality is due to significant growth of the values for the indicator group of culture-spiritual (patriotic) well-being that has grown by 24.48% [7]. According to the respondents, it is mainly due to prolonged action of the earlier investments in the creation of sport and recreation centers over the entire region and in the mobilization of patriotic spirit among young people.
The predicted and actual quantitations of the population life quality categories are shown pictorially in Figure 3.
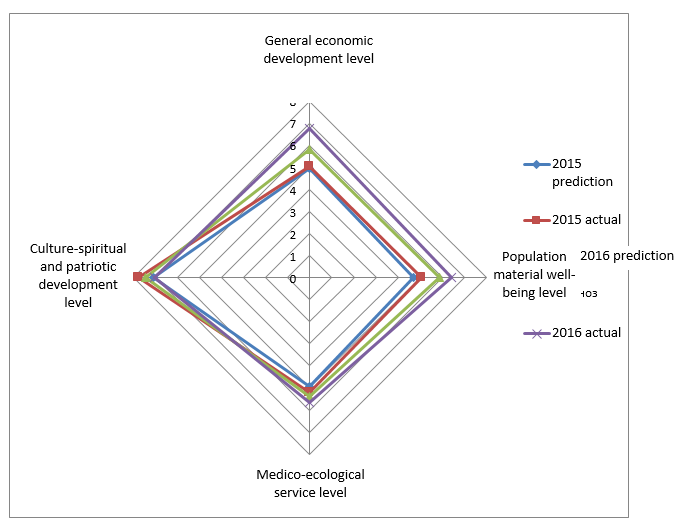
Figure 3. Sociological assessment of population life quality for 2015-2016 (prediction/actual)
Figure 3 data shows that by 2016 the satisfaction of population with the actual state of things in terms of the factor model of population life quality management was growing. All the categories were assessed above 5.57 scores on a scale from one to ten. By 2016, the people of the Nizhni Novgorod of Russia were satisfied with their material welfare assessed to be 6.41 scores and the general economic development level assessed to be 6.78 scores. The curve demonstrates pictorially the significant differences between the predicted and actual population life quality assessments in coordination of the components of the proposed factor model. Within this study.
The problem of evaluation of the direct influence by activity of the government and municipal authorities on population life quality is extremely severe and topical. The studies show that the population life level and quality are depending largely on both the revenues of population and other components of social activity. The factory model of population life quality management proposed by the author allows assessing the indirect impact of environmental factors on population life quality, using the quantitative indicators; and from the analysis of this impact, the main management solutions in the area of institutional and investment territory development policy can be formed.
References
1. Zakharova S. G., Maslennikov N. A. Money income generation assessment within the institutional transformations of population life quality at the rural and municipal districts // Innovations and investments. 2013. No. 3. p. 89-92.2. Zakharova S. G., Maslennikov N. A. The regular patterns of population life quality modification as an indicator of the institutional transformations in Russia// Economics and management of management systems. 2013. No. 2.1. p. 134-143.
3. Zakharova S. G., Kulagina E. N. Institutional innovative transformations of municipal district’s social branches// Bulletin of Nizhni Novgorod State University named after N. I. Lobachevski. No. 2-2. 2012. p. 141-149
4. Zakharova S. G. Socially-oriented human recourses management at rural and municipal regions and its influence on population life quality// Bulletin of Nizhni Novgorod State University named after N. I. Lobachevski. No 3. 2016. p. 7-16
5. Zakharova S. G., Maltsev A. N. Municipal region management system assessment in population life quality criterion// Power.No.8. 2016.p.67-73
6. Participative approach to increase in population life quality: Monography. Under the general editorship of N. M. Rimashevskaya, N. N. Ivashinenko. Nizhni Novgorod—Moscow: Publishing office of Nizhni Novgorod State University, 2013. – 268 pp.
7. Zakharova S. G., Sergeichev N. Yu. The population life quality modification tendencies at rural municipal regions under the influence of program budget// Increase in managerial, economical, social, and innovative technical potential of enterprises, branches, and people economic centers. Penza: Collected works of VIII International research-to-practice conference.2016. p. 31-36
