As you know, antibiotics are more than 70 years ago antibiotics to save human lives in the fight against deadly diseases. But many people do not know that with frequent use they can be the strongest allergen and impose irreparable harm to the body.
There are two ways to get drugs into the human body — with intentional use in the form of drugs or together with food consumed. The last problem of food pollution with antibiotics is known for a long time, but it was now that it became particularly relevant.
Preparations were widely used in animal husbandry, poultry farming and when growing fishing. They are used in the treatment of animals and birds, as well as they are included in the «growth hormones» used to increase the speed of growing livestock or bird. In disruption of the established conditions, antibiotics can get into milk, meat and eggs. For example, it will take 10-14 days from the organism of the animal to completely remove the veterenar drugs, and, accordingly, all side products obtained from livestock during this period should be disposed of [1].
As a result of permanent studies, many feed antibiotics are currently prohibited for use in animal husbandry and poultry farming due to the negative impact, which they are applied to the organism of animals and humans, and developing resistance to individual strains of microorganisms. However, some of them are still allowed as growth stimulants in Russia (tetracycline, griezin, bacitracin, tilosine). From the expertise of animal products, it follows that milk, beef, pork, poultry meat, meat products and food eggs are the most contaminated products [2]. Statistical data suggest that antibiotics are detected at 15-20% of all animal products.
At the stage of the technological process in the manufacture of food products, a significant part of the manufacturers is used to use special drugs for heat treatment, sterilization, filtering in order to increase storage time, to the cat Ors include milk and dairy products, meat, eggs, chicken, cheese, shrimp, and even honey.
According to the state report of Rospotrebnadzor «On the state of the sanitary and epidemiological good of the Olmachius of the population in the Russian Federation in the 20th 19 year» to the samples of the Water Eva products, not the corresponding sanitary and epidemiological requirements for the content of antibiotics, is presented in Figure 1 [3].
Centers of hygiene and epidemiology in the constituent entities of the Russian Federation for 2018-2019. 166,729 studies of food products were conducted with the purpose of identifying residual amounts of antibiotics, in the case of the presence of 18 antibiotics controlled in food products only according to information about their use (declaration). The diagram shows that those MP increase in relation to 20 12 am to -33.33%, from which it will listen to that the number of food products that does not meet the requirements of the relevant documents for the availability and exceeding the residual amounts of antibiotics decreased by 2019 in gradations with 2015, when a significant part of low-quality goods was revealed (59%).
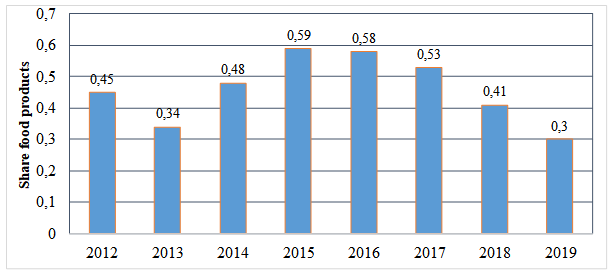
Figure 1. Food sample detection schedule, not relevant to the sanitary and epidemiological requirements for the content of antibiotics in the Russian Federation,%
Due to the fact that bacteria adapt to the action of antibiotics, such a phenomenon appears as antibiotic resistance, the essence of which lies in the fact that bacteria adapt and become resistant to the action of drugs. It is this effect that is most dangerous for a person, therefore it is very important that the nutritional Prod of Ukta, which it consumes daily, did not contain residual amounts of antibiotics, especially those similar to veterenar drugs.
One of the methods of solving the problem of contamination by antibiotics of food products can be increased overvailing of the quality of products, conducting laboratory tests into accounting laboratories and constant monitoring of the content of residual amounts of antibiotics of spinning groups [8].
Currently, new methods for removing antibiotics from finished products are being searched. It has been proven that a part of antibiotics is destroyed during heat treatment. Of these all thermal processing methods, the cooking in water is the most preferred option, since antibiotic moves from muscle fibers to the broth along with muscle juice and part of the drug is destroyed under the action of high temperatures. Therefore, it is very important to merge the first broth. Amoxicillin, chlorofacillin and tilosine, the concentration of which decreases greater than 50% [4] is susceptible to the greatest destruction under the action of large temperatures during cooking.
To remove antibiotics from water and sewage, scientists are trying to integrate advanced oxidation and gamma irradiation processes. In the future, you can integrate this method to remove antibiotics from milk and dairy products and beekeeping products.
Currently, a method is developed for the purification of milk contaminated with the antibiotics of the tetracycline group by making a hazed lime (SA (OH) 2) into milk. Subsequent purification from the resulting insoluble chelate salts of calcium is carried out by filtration [5].
This method allows to remove antibiotics from milk with a tetracycline group and direct the entire volume of milk-producing milk processing on the production of dairy products.
Another method that was developed by scientists from the Krasnoyarsk State Agricultural University, refers to the production of environmentally friendly meat of broiler chickens, in which the most often detecting the residual amounts of antibiotics. Broiler chickens aged 1 to 48 days daily in the basic diet are administered 0.45-0.50 g / kg of a living mass. An adaptogenic detoxification complex, which preinses the antiseptic stimulator of the road fraction No. 2 in the amount of 5 ml / kg of the complex, and At the age of 35-41 days, polyfepan is additionally introduced into the ration in the amount of 0.5-0.6 g / kg of alive mass daily.
The use of methods of detoxification and efferent therapy allowed to reduce the cytotoxic effect of a prolonged antibiotic, which was reflected in the decrease in the number of degenerative-changed hepatocytes and led to a decrease in the level of inflammatory infiltration in the interstice of the kidneys, in addition, there were no residual amounts of indisciotics in red meat [6].
There is not a single proven way of removing residual amounts of antibiotics from the finished food production products, therefore it is worth paying much attention to precisely this area, since it is here that most of the violations on the exceedable content of drugs are found. It is possible to study the electrophysical methods for processing products and methods associated with mechanical effects in more detail. Thus, the use of the electrostatic field can be attributed to the use of an electrostatic field, the use of current or low frequency currents, microwave — heating, IR — heating, the use of an atom energy, to the latter — processing of ultrasound products and the use of overpressure. Also, it is also necessary to use the option of using a sequential or parallel combination of these methods to achieve the goal.
Thus, from a large range of food products, the Naiba is an antibiotics prone to zoom, are exclusively priced of animal breeding, the birds of accession and B bars grown in the sacrons of your reservoirs. The problem of food pollution with antibiotics is very sharp and requires the search for new methods for the removal of residual amounts of antibiotics from finished products [7].
References
1. Antibe Iotics in the Food Evhi products. How to choose a safe food product? // Rospotr EBNNADORS URL: http://03.rospotrebnadzor.ru/content/185/553/ (d Ata handling: 19.03. 2021).2. Tatar Nikova N. A., Ma Ul O. G. Antibes Izyki in the Waters of Evhi products // Island of the Orenburg GA U. - 20 14. - No. 5 (49). - P. 208- 211.
3. State report "On Sanitary and Epidey of the Emiological Welfare of Nasya's Russian Federation in 20 19 year."
4. M Madalena C SOBRAL, ROBERTO ROMERO-GONZALEZ, MIGUEL A FARIA, SARA C CUNHA, ISABEL M P L V V O FERREIRA, ANTONIA GARRIDO-FRENICH STABILITY OF ANTIBACTERIAL AND COCCIDIOSTAT DRUGS ON Chicken Meat Burgers Upon Cooking and in Vitro Digestion // Food Chemistry. - 2020.
5. Patent of the Russian Federation No. 2016133953, 2016.08.18. Method of cleaning milk from tetracycline group antibiotics // Russian Patent No. 2666907. 20018. Bul. №81. / Merzlyakova K.A.
6. RF Patent No. 2003121721/13, July 14, 2003. The method of reducing cytotoxic action and the residual amount of antibiotics in meat chickens-broilers // Patent of Russia No. 2246849. 2005. Bul. №37. / Donkova N.V., Donkov S.A., Chumakov V.Yu.
7. Chaplygin O.S. Antibiotics in meat and meat products / O.S. Chaplygin, T.V. Perelegaeva // Safety and quality of agricultural raw materials and food: Collection of articles of the All-Russian Scientific and Practical Conference, Moscow, 2020. - P.87-88
8. Veterinary sanitary expertise with the basics of technology and standardization of animal husbandry products / Makarov V.A., Frolov V.P., Shuklin N.F. M.: Agropromizdat, 1991.
