he implementation of the concept of sustainable development requires implementation of complex of measures to ensure good environmental quality and ecological safety of production. However, the impact of the global impact of anthropogenic factors on the environment, primarily on the chiral purity of the biosphere has to date not developed fully. This is especially true of the economic aspects of the problem.
This circumstance is underscored by the fact that the environmental situation in Russia is characterized by extreme heterogeneity.
It should be noted that along with the fact that 7-8 million sq km in our country remain virtually untouched by modern business activity, more than 2 million sq km are recognized as environmentally unfavorable. Of course, it is precisely those areas where a significant portion of the population, is the most dirty business, especially in actively operated farmland. Emissions of polluting substances in atmospheric air, discharges of polluted wastewater, fugitive landfill, irrational use of pesticides and mineral fertilizers cause ever increasing pollution of soils and food [1-2]. This circumstance is underscored by the fact that the environmental situation in Russia is characterized by extreme heterogeneity.
It should be noted that along with the fact that 7-8 million sq km in our country remain virtually untouched by modern business activity, more than 2 million sq km are recognized as environmentally unfavorable. Of course, it is precisely those areas where a significant portion of the population, is the most dirty business, especially in actively operated farmland. Emissions of polluting substances in atmospheric air, discharges of polluted wastewater, fugitive landfill, irrational use of pesticides and mineral fertilizers cause ever increasing pollution of soils and food [1-2].
Development of theoretical and methodological foundations of long-term negative impact of anthropogenic ratemyserver effects on the chiral purity of the biosphere in order to ensure sustainable development of the territory represents a major socio-economic and national economic task, which determines the relevance of this study.
The relevance of this work is largely defined by a lack of methodology and the organizational-economic mechanism of state management of the ecosystems of the major industrial centers of the Russian Federation. In this context priority ecological-economic research is the scientific study of transition to sustainable development of the territory, ensure balanced solution of socio-economic goals for the future and preservation of favorable environmental quality, which implies the strengthening of the environmental component in various fields, harmonizing environmental and economic interests of society in the process of managerial decision-making.
The implementation of these issues requires the implementation of complex of measures on the new methodological basis, which determines the practical value of this study.
In terms of impact economic losses can be divided into direct and indirect. In this case, direct damages are the costs and losses that are directly related to anthropogenic impact and localization of their consequences. Indirect damage is associated with more remote in time losses.
An axiom in the economy of nature is the thesis according to which the economic damage caused by nature is considered to be random, stochastic variable. This means that indicators of environment-related losses cannot be estimated uniquely with a finite degree of accuracy, therefore, any assessment of damages should be described in terms of a greater or lesser degree of probability. Analysis of the definitions of «economic losses» allows to distinguish the following main forms of environmental harm: a) the loss of material goods or consumer properties created by the previous work; b) loss of (loss of) wealth or consumer properties when expenses incurred; C) the shortfall in the expected results when unrealized cost (loss of profit, unrealized potential); d) additional costs for compensation or prevent natural losses; d) inefficient use of available material and financial resources. In terms of impact economic losses can be divided into direct and indirect. In this case, direct damages are the costs and losses that are directly related to anthropogenic impact and localization of their consequences. Indirect damage is associated with more remote in time losses.
An axiom in the economy of nature is the thesis according to which the economic damage caused by nature is considered to be random, stochastic variable. This means that indicators of environment-related losses cannot be estimated uniquely with a finite degree of accuracy, therefore, any assessment of damages should be described in terms of a greater or lesser degree of probability. Analysis of the definitions of «economic losses» allows to distinguish the following main forms of environmental harm: a) the loss of material goods or consumer properties created by the previous work; b) loss of (loss of) wealth or consumer properties when expenses incurred; C) the shortfall in the expected results when unrealized cost (loss of profit, unrealized potential); d) additional costs for compensation or prevent natural losses; d) inefficient use of available material and financial resources.
The principle of minimizing impact on the environment during the sustainable development of production determines the balanced ecological-economic development of both individual objects and the territory in General.
The decision of problems of rational nature management is carried out from the standpoint of economic approach based on cost estimation of natural resources and approach, based on the definition of regulations of economic use of natural resources.
The most reliable way of determining the economy is the ecological optimum environment is a simulation of the interaction of the system «economy – environment», i.e., presents them in the form of models that simulate the behavior under certain conditions and within a specified time.
In our understanding of economic–environmental model suggests the option of maintaining ecological balance by reducing the impact of or regulation of production, taking into account environmental requirements.
Chiral purity of the biosphere is a necessary condition of the biosphere’s ability to replicate. Chiral (or mirror-antipode) are objects that do not possess a center or plane inversion. Mirror isomers (enantiomers), molecules usually called «left» (L) and «right» (D). Chiral purity is a property of the object (the environment) contain molecules of one type of chirality (either L or D). If the environment contains equally a mirror of opposites, it is racemic. Although inanimate nature «left» and «right» molecules are in equal amounts, the living organisms use only D isomers of sugars and L-isomers of amino acids.
The biosphere, as an open system located in a mirror-symmetric environment, should support their own chiral num-Toth, otherwise the system loses its ability to snowsprite Denia. There is experimental evidence of the link between loss of chiral purity of the metabolic networks of the organism and the occurrence of PA-tragicheskih States. So, it is established that the proteins of tooth enamel of people over 60 years rareminerals about 8% L-aspartic acid. When studying the process of racemization aspartic acid in the crystal structures of heavy molecular weight and insoluble proteins in the lens of the eyes of people of all ages found to have a large degree of racemization of amino acids in a more stable and «old» proteins of the cortex of the lens. This same phenomenon is noted in advanced cases of «brown» (Mature) cataracts, compared to «yellow» (immature). Chiral purity of the biosphere is a necessary condition of the biosphere’s ability to replicate. Chiral (or mirror-antipode) are objects that do not possess a center or plane inversion. Mirror isomers (enantiomers), molecules usually called «left» (L) and «right» (D). Chiral purity is a property of the object (the environment) contain molecules of one type of chirality (either L or D). If the environment contains equally a mirror of opposites, it is racemic. Although inanimate nature «left» and «right» molecules are in equal amounts, the living organisms use only D isomers of sugars and L-isomers of amino acids.
The biosphere, as an open system located in a mirror-symmetric environment, should support their own chiral num-Toth, otherwise the system loses its ability to snowsprite Denia. There is experimental evidence of the link between loss of chiral purity of the metabolic networks of the organism and the occurrence of PA-tragicheskih States. So, it is established that the proteins of tooth enamel of people over 60 years rareminerals about 8% L-aspartic acid. When studying the process of racemization aspartic acid in the crystal structures of heavy molecular weight and insoluble proteins in the lens of the eyes of people of all ages found to have a large degree of racemization of amino acids in a more stable and «old» proteins of the cortex of the lens. This same phenomenon is noted in advanced cases of «brown» (Mature) cataracts, compared to «yellow» (immature).
The human body is influenced by a large number of optically active substances (pesticides, insecticides, pharmaceuticals, PI-xevie additives, perfumes). Thus the enantiomers of the same substance have different, sometimes opposite effect on the functioning of metabolically active systems. Therefore they must learn not only to reduce environmental pollution, but in the end, to prevent the influence on the human body of racemates with an unknown biological effect, the effect of which can be fatal.
The process of racemization bio-organic substances and their rate of occurrence is significantly dependent on external conditions [3].
Analysis of the influence of negative anthropogenic impacts on the chiral purity of the biosphere was carried out in [4].
The biosphere is presented in the form of two interacting subsystems R and A, one of which (R) enables the production of a chiral substance by coming into it from the outside achiral substance and energy. The second (A) consists of objects used for self-reproduction of chiral substance subsystem R. the Consumption of L — enantiomers leads to the reproduction and consumption of  , D — to the loss of the object of this ability, his death
, D — to the loss of the object of this ability, his death 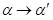 and transition
and transition ‘ to a subsystem of Р in the form of a racemate.
‘ to a subsystem of Р in the form of a racemate.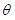 — the total number of chiral substrate,
— the total number of chiral substrate, 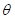 = L + D, and the -chiral order parameter of the subsystem Р,
= L + D, and the -chiral order parameter of the subsystem Р, 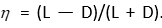 . The racemic condition of the correspond
. The racemic condition of the correspond  = 0; chiralmotion the state
= 0; chiralmotion the state 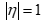 .
.
In the presented model of the biosphere, there are three steady States:
-
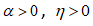 — in the biosphere there are living objects.
— in the biosphere there are living objects.
II.  , — the entire biosphere is represented by the subsystem P, which is in Giraldo polarized state.
, — the entire biosphere is represented by the subsystem P, which is in Giraldo polarized state.
III.  , -subsystem (A) is destroyed, a subsystem (P) fully racemized.
, -subsystem (A) is destroyed, a subsystem (P) fully racemized.
We studied the effect on the biosphere anthropogenic factors that have stochastic nature. It was assumed that recenserade stochastic effects can be entered into the model in the form of «white noise». From the biosphere were isolated bacteria and protozoa algae as the objects most susceptible to negative anthropogenic effects. Based on numerical studies of models identified for microorganisms important conclusions.
Further development of models of loss of chiral purity leads to the need of numerical analysis of the model identified for the processes occurring in microorganisms, in that case, if racemize stochastic factors represent the «color noise».
The object of the study are bacteria and protozoa algae, as the most exposed to anthropogenic factors. The importance of the functioning of bacteria and algae to the biosphere cannot be overestimated. None of the nutrient cycle is not without bacteria, so their livelihoods is a precondition for existence of life on the planet.
According to current estimates, the share of the ocean accounts for at least half of global primary production, expressed in the amount of fixed carbon. This primary production form algae, the only plants that inhabit the ocean. Algae are very important primary producers at the start of most food chains, including almost all marine and many freshwater circuit. These chain via zooplankton, crustaceans, etc. reach the fish. A microscopic algae — single celled, and they are major component of phytoplankton.
Fixation of carbon is only one of the consequences of photosynthesis. In addition, through photosynthesis, maintained the level of oxygen in the atmosphere, while at least half of all the algae emit oxygen, and their contribution to this process much more than the contribution of terrestrial forests.
However, phytoplankton biomass is low, often less than the biomass feed for his animals. This is possible thanks to an intensive metabolism, and photosynthesis of unicellular algae, providing a high growth rate of phytoplankton. Therefore, negative anthropogenic impact, preventing the growth of algae will affect many living organisms.
According to current data the total biomass of all plant organisms of the ocean is 0.3 billion tons of dry matter, biomass of animals of the ocean — 6 billion tons
The total biomass of bacteria and other microorganisms is expressed in significant quantities in the biocenoses sushi is superior to animal biomass (biomass of soil animals is approximately equal to 0.5 billion tons of dry matter, total biomass all other animal sushi 1-2 orders of magnitude less) .
Bacteria involved in cycles of all the biologically important elements and ensure the circulation of substances in nature. About 2 billion years ago, bacteria formed a biosphere, similar to modern. A key reaction of the nutrient cycle (e.g., nitrification, denitrification, nitrogen fixation, oxidation and reduction of sulphur compounds) are carried out only in bacteria. One g of soil contains hundreds of thousands or millions of bacteria in one ml of water — tens or hundreds of cells. In the upper layers of cultivated soil in 1 ha there is a few tons of bacterial cells. Mineralize plant and animal residues, microorganisms involved in the cycle of all the chemical elements composing the living cells. Thus, the source of carbon for higher plants and chemoautotrophic bacteria use the carbon dioxide of the atmosphere is fixed during the photo or chemosynthesis. The biomass of plants and animals are decomposed by microorganisms able to utilize cellulose, peptides, starch, lignin, pectin, ultimately to carbon dioxide and water.
As the role of bacteria in the nitrogen cycle. The atmosphere contains 79% nitrogen. It’s a pretty inert element, so that it is relatively rare in the bound state. Nitrogen is a necessary component of amino acids and proteins. No other element so does not limit the resources of nutrients in ecosystems, as nitrogen. It can become available to living organisms only in a bound form, i.e. as a result of nitrogen fixation.
Animals eating plants to synthesize proteins and other nitrogen-containing products in your body due to the protein plant. When mineralization of animal and vegetable protein putrefactive bacteria to form ammonia which is oxidized by nitrifying bacteria into nitrites and then into nitrates. As ammonium salts and nitrates serve as a source of nitrogen nutrition for higher plants, thus synthesizing proteins in your body.
The mineralizing ability of the bacteria provides to the cycle, and other biogenic elements (e.g. phosphorus and sulfur).
Bacteria differ changeable exchange, highly dropping with a lack of food. Under the influence of external factors (Ultraviolet rays, ionizing radiation, ailenin and other chemical substances), bacteria can lose their mobility, ability to form pigments, to give the debates, to increase or decrease the ability to synthesize various organic compounds, etc.
Meanwhile, a number of biochemical processes (glycolysis, electron transport, synthesis of aminoacids, proteins, nucleic acids, etc.) occurs in bacteria almost the same as in the cells of plants and animals. Synthesis of amino acids, proteins, nucleic acids represents an autocatalytic process.
The growth of bacteria depends primarily on the temperature, pH, availability of nutrients and ion concentrations [3,4].
Pollution of the biosphere with chemicals has a negative impact on microorganisms. For example, SO2 and H2S, passing the plasma membrane and penetrating into the cytoplasm, produce structural damage of the organelle membranes, in addition, inhibit and decompose the enzymes . All this leads to a reduction in the rate of autocatalytic processes.
This conclusion serves as a basis for further development and analysis of models of loss of chiral purity of the biosphere. It implies the need for quantitative research model identified for the processes that occur in microorganisms, with the aim of ascertaining the level of negative anthropogenic impacts that can lead the biosphere to environmental disaster.
The study of influence of negative anthropogenic factors on bacteria algae and protozoa (with the feasibility of the introduction of anthropogenic effects in the reaction of racemization and autocatalysis, going bacteria and algae) were obtained the following result [4]: while the long-term impact of negative anthropogenic factors on biosphere the most damaging effect of exposed single-celled organisms such as bacteria and algae, whose livelihoods is a necessary condition for the existence of life. Anthropogenic factors will influence the processes occurring in microorganisms, primarily on the autocatalytic reaction and the reaction of racemization.
This conclusion complements the quantitative research model that identified for processes in microorganisms. Accidental anthropogenic fluctuations were simulated there, using «white noise» [4].
We introduce in the system a multiplicative noise 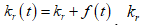 — given the rate constant of racemization substance subsystem Р. Here f(t) is white noise with zero mean and amplitude Н.
— given the rate constant of racemization substance subsystem Р. Here f(t) is white noise with zero mean and amplitude Н.
The numerical study shows that the state II the system is resistant to such fluctuations. For a long time even when the value of the amplitude H close to the critical one kr, the system is not out of status II.
In contrast, the system in state (I) significantly reacts to random changes of speed of racemization. Near the first critical speed values of racemization (bifurcation point), the system goes from state (I) in condition (II), i.e. from the biosphere disappear living objects and the order parameter remains positive.
The amplitude of the random fluctuations in this case may be less than the critical value of 5-6 orders of magnitude, i.e., stochastic effect even of very small amplitude can cause the disappearance of subsystem (A) living organisms.
In the transition system from (I), (II) the order parameter tends to a stationary solution of the form (II) corresponding to this value of speed of racemization.
This means that the transition from (I) to (II) occurs with fluctuations of the speed values of racemization and not due to the transition through the first critical value .
Entering into the system multiplicative noise  , K- the resource firething raw materials, g(t) — «white noise» with zero mean and amplitude H, obtain similar results. Condition (II) of the system will be resilient to such fluctuations, and the condition (I) near the first critical value will go into a state (II), and as in the previous case, the amplitude of the random fluctuations may be less than the critical value of 5-6 orders of magnitude.
, K- the resource firething raw materials, g(t) — «white noise» with zero mean and amplitude H, obtain similar results. Condition (II) of the system will be resilient to such fluctuations, and the condition (I) near the first critical value will go into a state (II), and as in the previous case, the amplitude of the random fluctuations may be less than the critical value of 5-6 orders of magnitude.
Effect on the biosphere with an exponentially-correlated random forces.
In this section we study the question of the impact on the dynamics of the chiral purity of the biosphere «colored noise», as more appropriate to real processes.
Considering the destruction of the chiral purity of the biosphere, as a model, in which the living objects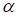 come from microorganisms, for the system of equations will take the following parameters:
come from microorganisms, for the system of equations will take the following parameters:
 .
.
Below investigates the impact on the state of the biosphere accidental anthropogenic factors expressed exponentially-correlated random forces.
We introduce in the system a multiplicative noise  . Here f(t) -is exponentially correlated goussinsky «colored noise» with zero mean
. Here f(t) -is exponentially correlated goussinsky «colored noise» with zero mean 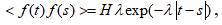 where Н — is the amplitude;
where Н — is the amplitude;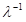 — the correlation time of random force. Then the equation for
— the correlation time of random force. Then the equation for 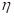 takes the form
takes the form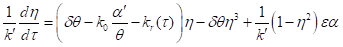 .
.
The numerical study shows that the condition (II) system, as in the case of white noise, is resistant to such fluctuations («color noise»). For a long time, even with fluctuations of the amplitude of the Н close to the critical value kr, do not take the system from state (II).
However, the condition of (I) the system reacts visibly to random changes of speed of racemization . Near the first critical speed values of racemization (kr 3.304*10-3 to 40.039 if
(kr 3.304*10-3 to 40.039 if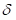 changes accordingly from 3.4*10—5 to 0.34) (bifurcation point) there is a transition of the system from state (I) in condition (II), which means the disappearance from the biosphere of living things
changes accordingly from 3.4*10—5 to 0.34) (bifurcation point) there is a transition of the system from state (I) in condition (II), which means the disappearance from the biosphere of living things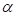 , the order parameter
, the order parameter 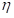 remains positive.
remains positive.
At the transition of the system from state (I), (II) the order parameter tends to a stationary solution of the system of equations of the form (II) corresponding to the selected value of speed of racemization. This means that the transition from state (I) to (II) occurs with fluctuations of the speed values of racemization and not due to the transition through the first critical value .
The bifurcation value kr equal 3.304*10-3 corresponds to the speed of racemization at which time pluralization still 0.2*10-3 year, the value 40.039 corresponds to the time of pluralization equal  year. The condition when a resource achiral material is K equal to 200 means that the response time of the autocatalysis still
year. The condition when a resource achiral material is K equal to 200 means that the response time of the autocatalysis still 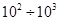 с. If the response time of the autocatalysis changes
с. If the response time of the autocatalysis changes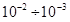 с, then K will change within
с, then K will change within 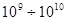 .
.
The decrease in the reaction rate of autocatalysis (which K = 200) possible, since it is known that increased razemicescuu cell environment leads to the decrease rate of synthesis of polynucleotides and protein .
Entering into the system multiplicative noise , where g(t) — exponentially correlated goussinsky «colored noise» with mean zero;
, where g(t) — exponentially correlated goussinsky «colored noise» with mean zero;
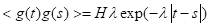 , H – amplitude,
, H – amplitude, 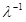 — the correlation time of random force; get the same results. The equation
— the correlation time of random force; get the same results. The equation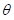 will look as follows:
will look as follows:

Condition (II) of the system will be resilient to such fluctuations, and the condition (I) near the first critical value K will go into a state (II).
Note that anthropogenic factors, introduced as a Delta-correlated random forces affect the chiral purity of the biosphere is much stronger than the negative impact, expressed as an exponentially-correlated random forces. For example, under the same parameter values, but when , that is, if the correlation time
, that is, if the correlation time  of the year., the time of the transition of the system from state (I) in condition (II) increases several times.
of the year., the time of the transition of the system from state (I) in condition (II) increases several times.
To simulate the impact on the biosphere «colored noise» system of equations it is convenient to Supplement the equation ,
,
where 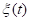 is white noise with zero mean,
is white noise with zero mean, . The equation
. The equation  for takes the form
for takes the form
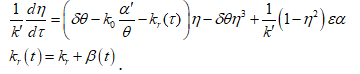
Similarly, when the equation
the equation 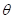 will look as follows:
will look as follows:
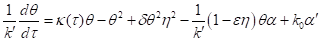 .
.
White noise was generated using the algorithm of Box-Muller using uniformly distributed random variables .
Conclusion. Summarizing the research it should be emphasized that the impact on living organisms in the biosphere a negative anthro-poganyj stochastic factors entered with as «white» and «colored» noise is extremely high. In a long-term impact of negative anthropogenic racemosus stochastic factors on the organisms an ecological disaster and the extinction of life on Earth can occur at speeds of racemization below (and for achiral resource material above) the critical (bifurcation) values. However, near the critical values under the influence of random deviations from the value of the speed of racemization (achiral resource), which is an exponentially-correlated random force with a fairly large correlation time, disastrous results in the microcosm will come much later than when the effects of time correlation which is close to zero.
References
1. Sukhorukova I. Economic-mathematical modeling of the optimal use of territories contaminated after the Chernobyl accident. International Journal of Professional Science. 2017. № 3. С. 21-28.2. Sukhorukova I. V., Vybornova, I. I., Vybornov A. N. Economic-mathematical model to analyze consequences of territory contamination. In the collection: Information technologies in education, science, technology and the Humanities inter-University collection of papers. Moscow, 2014. P. 203-210. (В сборнике: Информационные технологии в образовании, науке, технике и гуманитарной сфере Межвузовский сборник трудов. Москва, 2014. С. 203-210. )
3. Sukhorukova I. V., Vybornova, I. I., Vybornov A. N. MATHEMATICAL MODEL OF THE INFLUENCE OF TEMPERATURE AND CHEMICAL FACTORS ON THE FUNCTIONING OF CELLULAR RECEPTORS. Современный научный вестник. 2014. Т. 11. № 1. С. 38-45.
4. Vybornova, I. I. Vybornov, A. N., S. V. A. Mathematical modeling of the influence of stochastic ratemyserver effects on the chiral purity of the biosphere. In the book: the QUALITY of LIFE of the POPULATION AND the ENVIRONMENT, the Ministry of education and science of the Russian Federation, Penza state University, Penza state University of architecture and construction, Penza state agricultural Academy, interdisciplinary scientific-information center of the Penza state agricultural Academy. Penza, 2014. S. 176-188.
