Introduction
Sustainable development is crucial for all sectors of the economy, including industries such as the automotive sector. Presently, trends are going in the direction of a circular economy (CE) with less waste generation and decreased carbon footprints. Additionally, it will be a need to have a more rational utilization of natural resources. In this connection, great care has been given to the re-use of materials and components. Since the automobile sector is particularly one with high raw material and energy consumption in new vehicle as well as in spare part productions, the resulting large volume of waste poses challenges.
Currently, a substantial portion of auto parts is disposed of after use. However, modern practices show that many of these components can be restored and reused, offering both environmental and economic benefits. The objective of this article is to analyze the environmental and economic efficiency of reusing auto parts within the framework of CE principles.
Main part. Circular economy in the context of the automotive industry
The CE is a concept that focuses on the creation of sustainable economic models. According to this approach, resource consumption at any level should be optimized through the efficient use of products. The main focuses of the concept are the reusing and giving old life and new one of the used resources that reduce wastes hence generate positive economies (fig. 1).
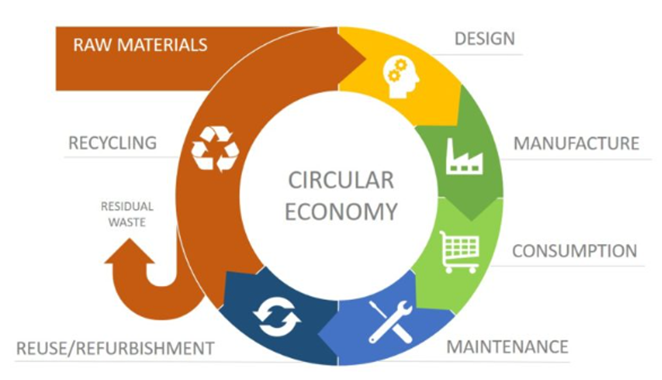
Figure 1. Model CE
The principles of CE are closed loops, waste minimization, and long-term resource utilization [1]. It is designed to optimize all processes, from design and production to disposal and restoration, thereby significantly reducing environmental impacts and increasing resource efficiency.
Closed loops in CE guarantee that materials and components will not become waste after their first use but will be returned to the economic flow by recycling, restoration, or reusing. The implication is less new resource extraction, hence reduced dependency on non-renewable raw materials and lower environmental impact related to resource extraction and processing.
Waste minimization is the basis of CE and depends on the fullest utilization of all materials at every stage of a product’s life cycle. This involves not only reducing excesses and waste but also improving production processes, which significantly reduces losses at each stage, from design to disposal. The production process needs to be optimized by the introduction of new technologies and methods, such as energy reuse, improved logistics, and the development of products that are easy to recycle or restore.
The long-term resource utilization principle involves designing products and components to last for a longer time and to be restorable or recyclable at later stages of their use. This calls for more durable and versatile products that can be modified or restored rather than being discarded or replaced. Such a policy also not only minimizes the wastes but reduces the production cost of new products as well, hence promoting more sustainable economics and lesser harmful impact on the ecosystem.
As the automotive industry is one of the largest users and generators of natural resources, there is vast scope for its potential to lead in the implementation of CE. Every vehicle consists of a thousand components that can be recycled or restored and thus reduces the need for extraction of new material resources to a great extent [2]. Energy intensity is really high to make auto parts with materials like steel, aluminum, plastics, and rare earths, so production in auto parts production involves a big impact on the environment. Thus, the transition to CE within the automotive sector enables a reduction in these costs and significantly mitigates the environmental impact.
Environmental efficiency of reusing auto parts
Reusing auto parts is a major aspect of environmental sustainability in the automotive industry, in light of increased challenges in waste disposal and depletion of natural resources. This process is efficient to the environment not only in reducing waste but also in minimizing negative impacts on the environment through reduction in demand for extraction of raw materials, improvement in energy efficiency, and lowering the greenhouse gas emissions. Implementation of the principles of CE in automotive services and companies is helpful for developing more sustainable and greener production practices.
The very important and major environmental concern regarding the reutilization of automobile parts refers to a very critical reduction of wastes that could arise from old vehicles and the materials they are made from. Each step of a vehicle’s lifecycle results in wastes: metal, plastics, rare earth elements that have applications in electronic systems. The application of reuse practices significantly reduces this waste by extending the service life of auto parts and components [3]. While the traditional model often involves disposal or partial recycling, CE emphasizes restoration and reuse, which dramatically reduces the overall volume of waste sent to landfills.
Improving energy efficiency and reducing greenhouse gas emissions are also critical aspects of the environmental efficiency of reusing auto parts. Recycling and restoring components such as engines or electronics require significantly less energy compared to manufacturing new parts. The restoration process often utilizes existing materials, reducing the need for additional raw material processing and minimizing energy costs. Additionally, restoring auto parts reduces carbon dioxide emissions associated with the extraction and processing of new materials, as well as energy consumption in their production. Technological advancements in component restoration, such as robotic systems and more efficient assembly methods, further enhance the energy efficiency of these processes.
Examples of successful environmental practices can be found in automotive service centers and manufacturers operating in accordance with CE principles. Tesla is actively engaged in the recycling of vehicle parts; a battery recovery program has been developed that significantly reduces dependence on the extraction of rare metals, particularly lithium and cobalt, in the production of new batches of batteries. The company’s battery recovery scheme provides for the collection, restoration, and reuse of materials, which minimizes the environmental impact during production [4].
Thus, reusing auto parts is a crucial tool for reducing the environmental impact of the automotive industry. Restoration and recycling practices provide significant advantages in waste reduction, resource conservation, energy efficiency improvement, and greenhouse gas emission reduction. The market for secondary parts continues to grow, and successful examples of companies operating under CE principles demonstrate the feasibility of integrating these practices on a broader scale in the automotive sector.
Economic efficiency of reusing auto parts
Adopting CE principles not only reduces costs but also creates new opportunities for growth and development in the secondary auto parts market. Reducing expenses related to materials, energy, and transportation leads to significant improvements in economic performance. Table 1 presents the economic benefits of restoring and reusing auto parts.
Table 1
Economic benefits of restoring and reusing auto parts [5, 6]
| Parameter | Auto parts recovery and reuse | Economic benefits |
| Resources and materials | The use of recycled materials such as metals and plastics. | Reducing the need for new raw materials and reducing production costs. |
| Energy consumption | Minimal energy cost for component restoration. | Reduced energy consumption, resulting in savings in operating costs. |
| The production process | Less time and cost for parts restoration. | Speeding up the production process, reducing labor costs. |
| Price for the end user | Refurbished spare parts are significantly cheaper than new ones. | Reducing the cost of car maintenance and repair for consumers. |
| Economic growth of the market | A growing segment of secondary auto parts has been formed. | Increased market availability and increased trade volume of secondary parts. |
| Business competitiveness | Providing cheaper solutions for car service stations and car owners. | Increasing the attractiveness of the company due to lower prices and high-quality service. |
| Jobs | Expanding the number of specialists in the field of recovery and recycling. | Creation of new jobs and development of the local economy, especially in regions with high rates of recovery. |
| General operating expenses | Lower costs for production, transportation and storage of spare parts | Lower operating costs by optimizing processes |
According to the author, the reuse of auto parts not only helps reduce production and transportation costs but also opens significant opportunities for market growth and stabilization. Resource savings, reduced energy consumption, and lower restoration costs provide companies with competitive advantages. The growth of the secondary parts sector stimulates job creation, improves the accessibility of auto parts for consumers, and contributes to the development of local economies. Collectively, these factors confirm the importance of integrating the principles of the CE into business models within the automotive industry to ensure long-term economic sustainability.
However, despite the growth of this market, challenges remain. One such challenge is the lack of sufficient regulatory frameworks for the certification and standardization of restored auto parts, which may lead to consumer concerns about the quality and safety of these components [7]. Additionally, the development of infrastructure for the efficient recycling and restoration of auto parts is a critical factor, requiring substantial investments in new technologies and equipment. Despite these hurdles, the secondary auto parts market continues to positively impact the economy and the industry as a whole, creating new business opportunities.
An example of a successful business model in auto part reuse is LKQ Corporation. The company has established itself as a leader in the automotive recycling industry by creating an extensive supply chain that sources, refurbishes, and distributes high-quality used and aftermarket auto parts. Through a combination of advanced inventory management, strategic acquisitions, and a commitment to sustainability, LKQ has optimized the reuse of auto components, reducing waste and lowering costs for consumers. In 2023, LKQ salvaged over 750,000 vehicles, sold over 12 million individual salvaged parts, and sent 116 thousand metric tons of product for recycling [8]. This large-scale operation highlights the company’s role in promoting CE practices within the automotive sector.
Thus, the reuse of auto parts offers significant economic advantages, including reduced costs for manufacturing new parts, the development of the secondary parts market, lower vehicle maintenance expenses, and job creation. These aspects enhance the competitiveness of companies and support sustainable economic growth, making CE an essential element not only in the environmental but also in the economic context of the automotive industry.
Conclusion
The reuse of auto parts, as a vital component of the CE, represents an effective mechanism for reducing environmental impacts and improving the economic performance of the automotive industry. Implementing its principles not only reduces waste and preserves natural resources but also lowers production, transportation, and restoration costs. Practices involving the reuse of auto parts have a positive economic impact, stimulating the growth of the secondary parts market, creating jobs, and enhancing the competitiveness of companies.
Successful examples demonstrate that integrating CE into the automotive industry can significantly increase business sustainability and profitability while improving environmental outcomes. In the future, the reuse of auto parts will not only be an environmentally justified approach but also an economically beneficial strategy for enterprises striving to reduce costs and establish sustainable business models.
References
1. Patel A, Singh S. Implementing circular economy strategies in the automobile industry–a step toward creating sustainable automobiles. Benchmarking: An International Journal. 2023;30(7):2225-2233. DOI: 10.1108/bij-08-2021-0486 EDN: LJFPXP2. Konstantinov DS, Solovyev KA, Gazizyanov AI, Sazonov AI. Implementation of environmental practices in business strategies: analysis of sustainable management models. First Economic Journal. 2024;7(349):133-141. DOI: 10.58551/20728115_2024_7_133 EDN: YCQFZL
3. Prochatzki G, Mayer R, Haenel J, Schmidt A, Götze U, Ulber M, Arnold MG. A critical review of the current state of circular economy in the automotive sector. Journal of Cleaner Production. 2023:13878 DOI: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.138787 EDN: VLNIAP
4. Li Z, Hamidi AS, Yan Z, Sattar A, Hazra S, Soulard J, Tailor F. A circular economy approach for recycling Electric Motors in the end-of-life Vehicles: A literature review. Resources, Conservation and Recycling. 2024;205:107582. DOI: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2024.107582 EDN: ILSPLJ
5. Stepanov M. Strategies for enhancing reliability and reducing energy consumption of electrical equipment in industry. Proceedings of the XLIII International Multidisciplinary Conference «Prospects and Key Tendencies of Science in Contemporary World». Bubok Publishing S.L., Madrid, Spain. 2024. EDN: GZAWRQ
6. Omair M, Alkahtani M, Ayaz K, Hussain G, Buhl J. Supply chain modelling of the automobile multi-stage production considering circular economy by waste management using recycling and reworking operations. Sustainability. 2022;14(22):15428. DOI: 10.3390/su142215428 EDN: WTJBGC
7. Abdullina L., Bobovnikova A., Zrazhevskiy A. ESG-factors and CSR-strategy impact on the investment attractiveness of USA companies. Proceedings of the XLIII International Multidisciplinary Conference «Recent Scientific Investigation». Primedia E-launch LLC. Shawnee, USA. 2023. EDN: EPFGKF
8. 2023 Sustainability Report. LKQ. URL: https://www.lkqcorp.com/sustainability/ (date of application: 29.01.2025).
