Introduction
The pandemic of COVID-19 became a major problem for the hospitality industry, forcing the industry to accept new realities and adopt innovative solutions. During this period, tourist traffic declined significantly, there was a massive number of hotel closures and massive economic losses. The recovery of the industry came with the accelerated digitalization, changing consumer behavior patterns, and increased competition.
In these conditions, the hospitality industry is transforming from traditional management and promotion methods to more dynamic and technology-based ones. The focus is placed on analytical software, demand forecasting, and omnichannel customer engagement strategies. Sustainable development is also an important aspect, making hotels more attractive to modern guests. The aim of this study is to analyze the evolution of the hospitality industry after the COVID-19 pandemic, unveil modern methods of sales, marketing, and management.
Main part. Sales in the hospitality industry in the post-pandemic period
The COVID-19 pandemic greatly impacted the hospitality industry, with a sudden drop in tourist service demand. From 2020 to 2021, hotel occupancy reached all-time lows, and hotel proprietors had to adapt to new realities by implementing strict sanitation practices and altering business models. The industry was, however, experiencing dynamic recovery by 2023, as measures were relaxed and practice in revenue management evolved (fig. 1).
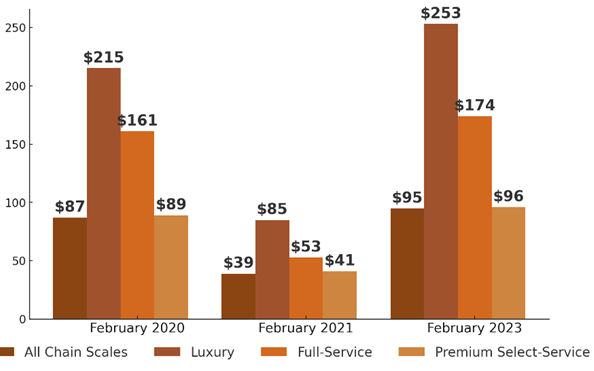
Figure 1. Revenue report in the hospitality industry by segments, overall RevPAR indicator [1]
In the recovery phase, changes in consumer behavior also played an important role. One of the causes of the demand growth was international tourism rebounding. After two years of strict restrictions, travelers were ready to make up for lost ground on recreation opportunities, and reservations picked up dramatically. No less important in the industry’s recovery was the strengthening of domestic tourism.
In the post-pandemic period, there is also a special focus on revenue management techniques and price flexibility. Models based on fixed rate and seasonality are outdated, replaced by dynamic. This allows hotels to respond quickly to changes in demand and competition. One of the most valuable tools in this area is Revenue Management, where predictive analytical solutions and automated rates are derived from data inputs of hotel occupancy, season, consumer demand patterns, and macroeconomic factors. Large hotel chains have employed artificial intelligence (AI) and big data solutions to more accurately predict the direction in price and control their rates. Use of these technologies allows not only the response to tendencies in the market in real time but also the offering of personal prices for different groups of customers. For example, depending on machine learning algorithms, the system can examine past reservations of guests and offer personal discounts or additional services, thereby guaranteeing customer loyalty and profitability for the company [2].
Another important trend in the hospitality industry since the pandemic has been the proliferation of subscription schemes and regulated tariffs. There are hotels that offer guests the possibility of a monthly subscription for accommodation, which is especially convenient for remote employees and corporate clients. These schemes allow flexible budget planning and ensure constant hotel occupancy during periods of fluctuating demand.
Development of digital technologies and the change in consumer behavior led to the extinction of traditional sales channels, such as phone booking and agency networks, and they have been replaced by an omnichannel. Hotel chains are making more investments in the establishment of direct sale channels like websites and mobile apps. Through this manner, they can reduce reliance on intermediaries and lower commission outlays. Booking.com, Expedia, and Google Hotel Ads remain important drivers of traffic and conversion for hotels, especially within the independent hotel category with poor brands.
Another important trend after the pandemic is the emergence of new types of housing. Hybrid hotels that combine elements of coworking, long-term rental housing and traditional hotel services are gaining momentum. They are more popular in urban areas, where high demand for medium- and short-term rental housing reduces the applicability of traditional hotel models. In addition, serviced apartments are becoming more and more in demand, which provide travelers with the opportunity to stay longer, as well as the opportunity to cook their own meals and use additional amenities [3].
Thus, the evolution of hospitality sales in the post-pandemic period is linked to the emergence of modern technologies, dynamic pricing, and changes in distribution channels. Under the conditions of intense competition and changing demand, hotels must adapt to the new reality of the market by offering customers personalized solutions, automated services, and new models of interaction.
The evolution of marketing strategies in the hospitality industry in the post-pandemic period
The post-crisis period has changed solutions to the issue of marketing strategy and customer relationship in the hospitality industry. Ecological tourism, safety, personalized services, and the application of interactive technologies became the conditions of competitiveness. Development of digital marketing has also undergone changes: video, social networks, and blogs have become obligatory advertising tools, and AI has made the ads more aimed and personalized. Table 1 gives a compilation of major changes in marketing strategies in the hospitality industry in the post-pandemic period and discusses their impact on the industry.
Table 1
The evolution of marketing strategies in the hospitality industry [4, 5]
| Direction of change | Description of the changes | Impact on the hotel industry |
| Environmental and social responsibility | Implementation of «green» standards, reduction of plastic waste, use of renewable energy sources. | The growing popularity of environmentally responsible hotels, reducing operating costs, and attracting conscious travelers. |
| Digital marketing | Using Internet platforms to personalize advertising campaigns and target customers. | Increasing audience reach, strengthening competitive advantages, and increasing the effectiveness of marketing investments. |
| Interactive technologies and new advertising channels | Development of virtual tours, AI recommendations, enhancement of video content, collaboration with bloggers and opinion leaders. | Increased user engagement, improved customer experience, and increased direct sales. |
| Customer loyalty and omnichannel communications | Flexible loyalty programs, cumulative bonus systems, integration with chatbots, social networks and mobile applications. Development of subscription accommodation models. | An increase in the number of regular customers, speeding up the booking process, and improving the usability of services. |
These technologies have become the primary change drivers in the marketing industry. Through them, new standards of customer engagement are being developed, enhancing the competitiveness of the hospitality industry. Hilton Hotels & Resorts is one such company that has brought about evolutionary marketing strategies. It launched a program that increased sanitary safety standards, as well as demonstrating the active use of AI in creating promotional campaigns. These initiatives helped the chain build customer trust, increase bookings, and solidify its competitive advantage [6].
New approaches to hotel business management
In the post-pandemic period, the hospitality industry is witnessing transformations that demand a complete restructuring of guest services and management methodologies. The most important among them was the universal implementation of contactless technologies that reduced contact between staff and visitors to an all-time low. Mobile and digital check-in have become the industry standard for a majority of hotel chains. By the check-in procedure, visitors are able to use the app on their mobile phone and then use their phones to open the doors, thereby not only saving time but also avoiding queues at reception [7].
An important part of the technology shift has been the development of the «smart room» technology, which entails Internet of Things technologies. Climate control, lighting, and multimedia systems can be controlled by the visitors using voice commands or intelligent devices. The hospitality industry is also actively adopting robotics and process automation.
The COVID-19 pandemic caused a complete revamp of safety procedures and sanitary standards in the hospitality sector. Compliance with rigorous hygiene measures is now a key factor in guests’ decisions when selecting a hotel, and transparent disclosure of the security procedures being implemented boosts confidence in the brand. New sanitary protocols, including increased disinfection of properties and the use of antimicrobial coatings, have been developed and implemented by hotel chains [8]. Most of them have invested in automatic hand sanitizer dispensers and disinfection systems that provide instant sanitization of public areas and bedrooms.
Employee training on new security procedures has been made mandatory, including routine training on hygiene rules, proper use of personal protective equipment, and contact reducing measures for visitors. Some hotels have incorporated monitoring of employees’ health through digital means, reducing the viral transmission risk. In addition, hotels use quick response codes and electronic dashboards, through which the travelers are able to view information on hygiene measures taken, latest cleaning dates and safety protocols. All these technologies enhance the openness of the service and provide safety to the guests while they stay.
The pandemic pushed the hospitality industry to be innovative within the face of changing economic realities, compelling a re-examination of current business models and a focus on operational effectiveness. Cost optimization and digital solution adoption helped hotels reduce costs without compromising on service levels. One of the main directions has been the introduction of cross-functional duties for staff. In smaller hotels, receptionists now combine the functions of concierges, and housekeeping staff work according to an optimized schedule that aligns with the hotel’s occupancy.
Special attention is given to inventory and supply chain management. Predictive logistics based on AI are being implemented within hotels to produce accurate predictions of material and product demands. Hotels may opt to utilize local suppliers in certain instances, providing a more agile, lower-cost, and safer procurement method. Hotels are also investing more in energy-efficient solutions. The applications of water recycling units, motion sensors, and programmable thermostats not only conserve money but are simpler to operate earth-friendly programs.
The pandemic’s issues that the hospitality industry faced created manpower reductions, which were detrimental to the industry’s recovery. It was hard for most of the hotels to retain and hire skilled staff, and this had them adopting new methods of dealing with employees and company culture. Hybrid work models were one of the solutions implemented. In large hotel chains, customer service staff can now work remotely, and booking and call centers are partially automated with AI chatbots. Changes in business processes also led to new qualifications requirements for employees. Companies have started actively investing in staff training, including digital technologies, customer service, and data management training. Additionally, employee support programs and corporate culture strengthening are being developed.
Hotel business management after a pandemic requires an overall response through various means like digitalization of business, application of new cleanliness norms, and adaptability of the management towards handling people. Hotels that actively adopt innovative practices and adapt to evolving consumer trends gain a significant competitive advantage within the transformed economic landscape.
Conclusion
The post-pandemic period was a period of revolutionary changes for the hospitality industry, and it had to rethink a variety of traditional management, marketing, and sales approaches. Adaptations to new economic and sanitary conditions, innovations of digital technologies, and price adaptability are the main drivers of the recovery process. Hotel executives who successfully utilize such strategies demonstrate profitable expansion in the face of unstable demand and intense competition. Notably, innovations in services and marketing allow for a more tailored and secure experience for visitors.
References
1. The Pandemic and the Hospitality Industry: From Impact to Recovery / The Plasencia Group // URL: https://tpghotels.com/the-pandemic-and-the-hospitality-industry-from-impact-to-recovery/ (date of application 10.02.2025).2. Moroz K. Using key performance indicators (KPI) for developing growth strategies and managing company performance // Znanstvena misel journal. 2024. № 96. P. 27-29. DOI: 10.5281/zenodo.14242184 EDN: LWQEAY
3. Yudha A. T. R. C., Basya M. M. Adaptive Business Model in the Post-Pandemic Era of Covid-19: Evidence in Greensa Inn //Indonesian Interdisciplinary Journal of Sharia Economics (IIJSE). 2024. Vol. 7. №. 1. Р. 15-32.
4. Vanegas-López J. G., López-Cadavid D. A., Mathew M., Vo-Thanh T., Restrepo-Morales J. A., Sthapit E. Bounce-back strategies: Revitalizing the hotel industry post-pandemic //Tourism and Hospitality Research. 2024. Р. 14673584241277019.
5. Nazarova Ye.K. THE IMPACT OF MENTAL HEALTH ON WORK PRODUCTIVITY // Universum: Psychology and Education: Electronic scientific journal. 2024. No. 7(121). URL: https://7universum.com/ru/psy/archive/item/17860 EDN: WOSGLE
6. Fachada B. C. Business adaptive strategies in crisis: the case of Hilton Hotels Worldwide: – 2023.
7. Prentice C., Tracogna A., Akbar Y. H. The Paths to an Enhanced Ecosystem for International Hotel Chains //Journal of the Knowledge Economy. 2024. Р.1-25. DOI: 10.1007/s13132-024-02579-4 EDN: ZPENAM
8. Kidassova M. Business scaling strategies in international markets: Analysis of expansion and localization models // Cold Science. 2024. № 10. P. 7-14. EDN: LMKFML
