The global energy sector is on the verge of technological and structural reforms. According to the World Economic Forum, digitalization of the oil and gas industry alone can bring additional income. However, this technological transition can be a very painful transformation for many old industrial enterprises.
It is increasingly common to hear that information technology is the new oil. Those who learn how to turn information arrays into useful solutions will benefit, and vice versa, those who miss these opportunities will remain in place, maybe even forever. If this applies to any business, then in the oil and gas industry, which plays a key role in the country’s economy and has huge but not yet realized opportunities, combining traditional baggage of experience, skills and knowledge with new innovative solutions based on modern information technologies can have a tremendous synergetic effect.
Actually, the choice of this path is predetermined, because the world’s leading energy companies, which began to introduce digital technologies at the beginning of the 21st century, have already received a significant start in the competitive market, they have energetic followers on a smaller scale [1].
Russian oil companies are only at the stage of their development, and further delay may cost them the loss of competitive positions, as «digitalization» allows them to solve problems faster, more economically and with fewer risks, and expands the horizons of opportunities.
For example, State Atomic Energy Corporation ROSATOM, realizing that it needs to expand the horizons of its capabilities, is already implementing the following technological achievements:
- Quantum communication technologies;
- Virtual and augmented reality technologies;
- new production technologies;
- Neurotechnology and artificial intelligence;
- Wireless communication technologies.
Over the past three to four years, Russian oil companies have achieved significant success in mastering digital technologies and using them in various fields of professional activity. The digitalization of the oil and gas industry is primarily aimed at enabling prompt risk-based decision-making, as well as improving the company’s productivity and value.
PJSC ROSNEFT Oil Company has created a unique platform for the development of digital technologies in the oil and gas industry. Being one of the leaders in the field of business process informatization, the company holds a scientific and technical seminar «Digital technologies in field development».
The company intends to further develop its own competencies in the field of digitalization and innovative technologies. The scientific and technical seminar, organized on the basis of the «RN-UfaNIPIneft» Institute, has become an annual scientific discussion platform for discussing the most pressing problems of the domestic mining industry. This made it possible to reduce the dependence of the Russian oil and gas industry on foreign software products and increase the efficiency of production processes [2].
The digital economy creates a digital ecosystem that changes priorities and values. The new priorities and values of the digital economy may have a greater impact on competition in the global market, including oil, than breakthrough digital technologies. China, Singapore, New Zealand, South Korea and Denmark are among the leading countries in terms of digitalization of the economy. Canada is creating an information and communication center in Toronto.
Singapore is building a smart economy driven by information and communication technologies. South Korea is implementing the Creative Economy program, aimed at developing human capital, entrepreneurship, and the dissemination of information and communication technologies. Denmark is actively investing in the digitalization of public authorities. According to the Boston Consulting Group, today Russia ranks 35th in the world in terms of the development of the digital economy.
Without digital technologies, modern society can no longer imagine its life. Digitalization has been introduced into completely different fields of activity, using cloud technologies, technologies for processing large amounts of data, the Internet of things, virtual and augmented reality, etc. Digitalization is the creation and implementation of intelligent mechanisms that not only create a digital economy, but also allow people to live in smart homes, cities, etc. All industries have the potential for digital transformation, but the fields of activity related to information and communication technologies are easier to handle.
The problem of digitalization is attracting special attention today, as it plays a role in the development of social institutions, the organization of daily life, and the socialization of the individual. First of all, there are obvious changes in a person, culture and social space, which are expressed in the restructuring of thinking, perception, communication, language, living space and socialization [3].
Digitalization is entering our lives at a tremendous rate, which is primarily due to its possible positive impact at all levels. So, at the level of the entire modern society, the result and positive consequences are:
- the emergence of new business models and new forms of business;
- economic and social impact on business and society;
- ensuring the possibility of monitoring economic transactions, which leads to increased transparency;
- productivity growth of the entire social labor due to its increase at the level of individual companies;
- automation of production due to the emergence of human replacement systems.
The introduction of digital platforms is fundamentally changing the way businesses are organized and economic processes are managed. Representing the result of a high level of informatization of society, digitalization creates new technological opportunities for the further development of the global economy. Therefore, the researchers note that «digitalization has a profound impact on global trade and investment, transforming economic industries and sectors around the world.» Obviously, in modern society, the concept of the «digital economy» is no longer a purely theoretical construct, but is taking on distinct forms, manifested in the emergence of electronic payment systems, online commerce, online banking and other information services. Figure 1 shows the interaction scheme of the participants of the Digital Economy program.
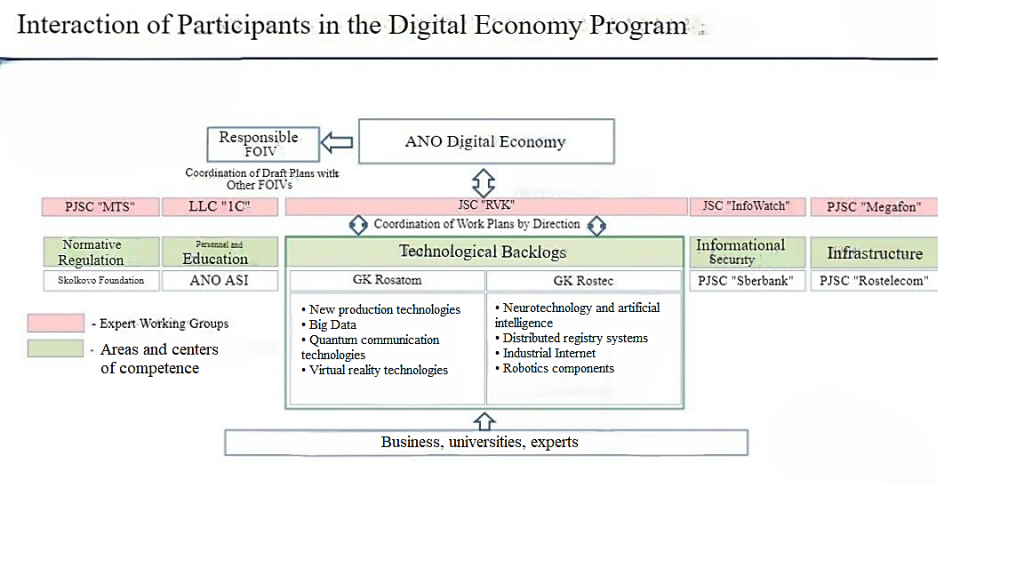
Figure 1. The scheme of interaction of participants of the Digital Economy program
As can be seen from the figure, the introduction of digital technologies throughout the supply chain facilitates the simplification and synchronization of processes, as well as a comprehensive review of decision-making circumstances in the global practice of digital transformation of oil and gas companies.
For example, to accelerate companies’ adaptation to the realities of the digital economy, a number of foreign countries use tax incentives to write off expenses on hardware and software. For example, in the United States, they invest in servers and hardware; in Australia, the government invests in public broadband access, the Internet, scientific research, and the creation of a regulatory framework.
The trends and pace of change taking place in digital oil and gas technologies never cease to amaze us [4].
The development of the oil and gas industry in a digital economy is a more serious challenge than the introduction of digital oil and gas technologies. Unconventional or alternative energy sets new boundary conditions for the oil and gas industry.
The digital oil and gas economy is a new paradigm of accelerated capitalization and economic development of oil and gas companies and the industry as a whole; high–quality satisfaction of demand for oil, gas and petroleum products without intermediaries in real time.
Back in late 2017, The Boston Consulting Group identified four breakthrough tools in the digital economy: «digital privatization», «digital leap», «self-digitization» and «digital reinvestment». These tools will allow oil and gas companies to better structure their technological initiatives and ensure that their economies enter a competitive and sustainable trajectory at an accelerated pace.
The first tool of «digital privatization» is to eliminate areas of inefficiency in order to free up resources and increase the competitiveness of the industry. The problem is solved with the help of those oil and gas companies that are most interested in accelerating their development and competence to achieve results.
The second tool, the digital leap, arises from the creation of new oil and gas businesses and the rapid development of the use of advanced technologies in the oil and gas business: technologies of «big geodata», artificial intelligence methods and blockchain.
The third tool, the «proprietary digitization» of the oil and gas complex, makes it possible to increase the efficiency and transparency of all processes of interaction between oil and gas companies and the state, to simplify doing business in the country, which creates a significant positive effect for the oil and gas industry.
The fourth tool is the «digital reinvestment» of profits earned from the sale of the first three devices due to a significant increase in added value, lower operating costs and increased efficiency of oil and gas production. The National Technology Initiative is the development of the digital economy [5].
The development of the digital oil and gas economy and the promotion of modernization of oil and gas production will largely depend on government policy. The introduction of blockchain technology will allow for a deep modernization of the oil and gas market, simplify the interaction between supply and demand, neutralize the influence of intermediaries – international oil traders and simplify trade in oil, gas and petroleum products between the Eurasian Economic Union countries.
The main trend of changes in oil and gas technological processes is the increasing role of mechanization, automation and the replacement of manual and unskilled labor by machines, technological complexes and qualified specialists. The digital oil and gas economy is a social work and economic activity in the oil and gas industry, in which more than half of its own gross domestic product is accounted for by the cost and value of tangible assets – products (oil, gas, petroleum products, etc.) and oil and gas services (information and communication, drilling, logistics, etc.) created by robotic systems. The main trend of changes in oil and gas technological processes is digitalization, intellectualization, optimization and robotics, and the gradual replacement of jobs with robotic systems.
The medium–term digital development strategy of an oil and gas company is a strategy for modernizing oil and gas production into a digital ecosystem, realizing the potential of digital technologies by creating new products and services, changing the ways the company interacts with the environment, and changing the ways employees interact with the means of production and with each other in real time. The rapid adaptation of digital oil and gas technologies is characterized by short innovation cycles.
As you know, the development of the oil and gas economy is measured in points of increase or decrease in Russia’s GDP. It is a metric unit of measurement for the industrial economy. Digital oil and gas production needs a different metric, which is much more sensitive to the constant emergence of new digital oil and gas technologies, equipment and machinery [6].
Thus, digitalization has a significant impact on the development of the oil and gas industry, opening up new horizons for additional income. The introduction of modern technologies such as blockchain, mechanization and automation of labor allows companies not only to optimize their operational processes, but also to develop new business models that can significantly increase profitability.
Examples of successful digitalization show that companies that actively innovate can manage their assets more efficiently, reduce costs, and improve the safety of production processes.
In the future, companies that can adapt to the rapidly changing conditions of the digital economy will have clear competitive advantages. Investing in digitalization will not only help improve financial performance, but also create new opportunities for growth and development. Thus, in order to function successfully in the context of digital transformation, oil and gas companies need to actively seek and implement innovative solutions that will allow them not only to survive, but also to thrive in the face of global competition.
The global oil and gas industry is constantly searching for new technological solutions that can increase efficiency and reduce costs, and survive a period of low prices. For most companies, using innovation is not just a tribute to new trends and trends, but a matter of survival.
The introduction of digital technologies throughout the supply chain facilitates the simplification and synchronization of processes, as well as a comprehensive review of decision-making circumstances in the global practice of digital transformation of oil and gas companies.
The largest players in the oil service segment and equipment suppliers have traditionally competed due to low prices, rather than due to unique technological solutions. Many of them have been affected by falling prices and stricter customer policies and are unable to invest in new products and competencies. In general, they rarely initiate cooperation in the field of digitalization of Russian vertically integrated oil companies. The sanctions, of course, have given impetus to the development of import substitution, and it is safe to say that changes in this area may be seen in the near future.
References
1. Большов, М. А. Тренды цифровой трансформации нефтегазовой отрасли на современном этапе / М. А. Большов, Г. И. Железняк // Научные открытия: междисциплинарные аспекты : Сборник статей II Международной научно-практической конференции. – Москва: Издательство ЦДПО «Цифровая академия», 2024. – С. 343-347.2. Иринина, А. Ю. Влияние цифровизации на развитие российских нефтегазовых компаний / А. Ю. Иринина, И. В. Баскакова // Весенние дни науки : сборник докладов;. – Екатеринбург: Уральский федеральный университет имени первого Президента России Б. Н. Ельцина, 2021. – С. 662-666.
3. Ширяев, А. Д. Актуальные проблемы кадрового обеспечения топливно-энергетического комплекса российской Федерации / А. Д. Ширяев, А. И. Соболевская // Молодежь, образование и наука XXI века : Материалы научно-практической конференции студентов и аспирантов, посвящённой памяти заслуженного деятеля науки РФ, профессора В.С. Соминского. – Санкт-Петербург: Санкт-Петербургский государственный университет промышленных технологий и дизайна, 2023. – С. 62-66.
4. Абдуллаев, Р. Ф. Цифровая трансформация нефтегазовой отрасли: проблемы и перспективы / Р. Ф. Абдуллаев // Актуальные вопросы современной науки : Сборник статей VII Международной научно-практической конференции. – Пенза: Наука и Просвещение (ИП Гуляев Г.Ю.), 2023. – С. 27-29.
5. Дудникова, С. А. Использование виртуальной и дополненной реальности в обучении инженеров / С. А. Дудникова, О. В. Борисова // Современное инженерное образование: вызовы и перспективы : Материалы III национальной научно-практической конференции – Магнитогорск: Магнитогорский государственный технический университет им. Г.И. Носова, 2024. – С. 129-132.
6. Борисова, О. В. Перспектива развития надежности информационно-управляющих систем / О. В. Борисова, Р. И. Каримов // Перспективы развития технического сервиса в агропромышленном комплексе : сборник материалов Всероссийской (Национальной) научно-практической конференции с международным участием, посвященной 60-летию создания кафедры технического сервиса (ремонта машин и технологии конструкционных материалов). – Чебоксары: Чувашский государственный аграрный университет, 2024. – С. 18-20.
