Social activities and activism play an important role in the modern world, allowing people to come together to solve social, political and environmental issues. However, the psychology of activists and those involved in social work often remains poorly understood.
This article will examine the key features of the psychological profile of people actively participating in various public initiatives. Understanding the psychology of activists will help to better assess their role in modern society and find effective ways to support and develop a social movement.
An activist is an active member of an organization, an active participant in a social movement [1].
Student activists are a group of students who independently resolve issues related to the lives of students in organizing education, everyday life, and leisure.
An activism is a means of self-realization and development of initiative.
First of all, a key role in a person’s interest in any type of activity is played by his motivation. Everyone finds something in their work that motivates them to do this work. Motivation is like the driving force that makes us want to do something. It is a complex process that involves balancing our various needs and desires, as well as reflecting on the results of our actions [2].
We conducted a survey among 60 student activists of the St. Petersburg State University of Industrial Technology and Design, Higher School of Technology and Energy, which consisted of collecting those factors that motivate them to engage in social activities (Figure 1).
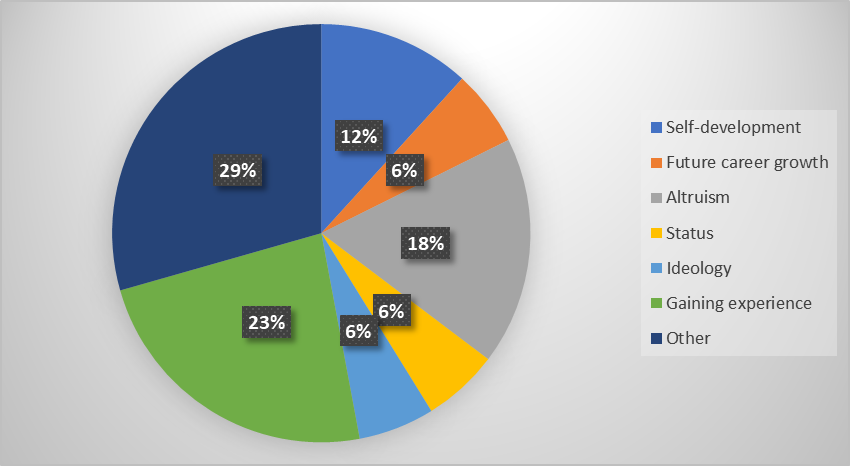
Figure 1. Results of a student survey: «What is your key motivation in social activities?»
The survey results showed that the main motivation for engaging in social activities among respondents is varied. The largest number of survey participants (23%) noted that their key motivation is to gain experience in working with people and organizing events. For 18% of respondents, an important factor is altruism – the desire to help others. Self-development also turned out to be significant with 12% of participants who want to improve their personal, leadership and professional qualities indicating it as their main motivation. Career growth, status and ideology were chosen by 6% of respondents respectively. A significant number of respondents (29%) indicated “other” as their key motivation, which may indicate a variety of factors that motivate people to engage in social activities.
Let’s focus on the group of people who choose empathy and altruism as their motivation because they strive to create a positive impact on others, help others, and develop deep interpersonal connections that contribute to a more friendly and supportive society.
High levels of empathy are a key feature of activist psychology. Thanks to high empathy, activists can build deeper and more trusting relationships with others, and show concern and understanding for the needs of other people. This helps them more effectively maintain social connections, participate in various public initiatives and influence processes of change in society. A high level of empathy also contributes to the development of emotional intelligence in activists, which allows them to better understand themselves, their emotions and reactions, and also respond appropriately to the emotional states of other people. This important quality helps activists build cooperation, resolve conflicts and achieve common goals in a team [3].
People who participate in activism and social activities often exhibit distinctive psychological characteristics that contribute to their motivation and sustained participation. These features include the following.
- Activists are often motivated by a desire for personal growth and development. They view their involvement in social causes as an opportunity to learn from others, develop their leadership skills and contribute to their own well-being.
- Socially concerned people have different views on career development compared to traditional professionals. They can take on leadership roles to improve their ability to influence change.
- Activists have strong beliefs and values that guide their actions. These ideologies can range from the environment to social justice and can shape their priorities and decision making. Ideology can also provide a sense of purpose and belonging in social movements.
- Gaining experience is one of the key aspects for socially employed people involved in social activities. Participation in various projects and initiatives allows them to broaden their horizons, develop communication, leadership and organization skills, as well as learn to work in teams and solve problems effectively.
The experience gained in the course of social activities helps activists better understand social problems and mechanisms for solving them, as well as formulate their vision of the future and the goals they strive for. In addition, participation in various events and projects allows activists to create valuable connections and contacts, which can be useful for both personal development and future careers. Thus, gaining experience in various projects and initiatives is the basis of social activities [4].
Another basis of social activity is effective communication between people. It allows you to convince, inspire and unite people around common goals. The ability to clearly and effectively express one’s thoughts and ideas is an important tool for influencing public opinion and mobilizing initiatives. Communication is the bridge that connects activists with a wider audience, allowing them to convey their ideas and values to other people. Properly structured communication helps not only to avoid conflicts and disagreements, but also increases the interest of participants in the work. Speaking about effective communication, we also mean joint leisure. The students surveyed also confirmed that meetings of colleagues in an informal setting strengthen their relationships with each other and have a positive effect on their future work [5].
But unfortunately, effective communication does not completely minimize conflicts in the group. In social activities, activists face various troubles that can cause stress and lead to quarrels. To combat conflict situations in the group, some rules were developed. Let’s consider them.
- It is important to take time for rest, physical activity, healthy eating and sleep to maintain your physical and emotional health.
- A structured approach to work, setting priorities and rational time management helps reduce stress levels.
- Meditation, yoga and other relaxation methods help reduce stress and improve psychological well-being.
Another, perhaps the most relevant, factor influencing the emotional state of an activist is burnout. It may include feelings of fatigue, lack of motivation, frustration, decreased productivity, and feelings of cynicism about work or responsibilities. Some typical signs of burnout include feelings of powerlessness, frustration, feelings of failure, apathy and emotional exhaustion. About 60% of students surveyed confirmed that they experienced burnout during increased workload. They also identified several factors that allow them to avoid emotional exhaustion [6].
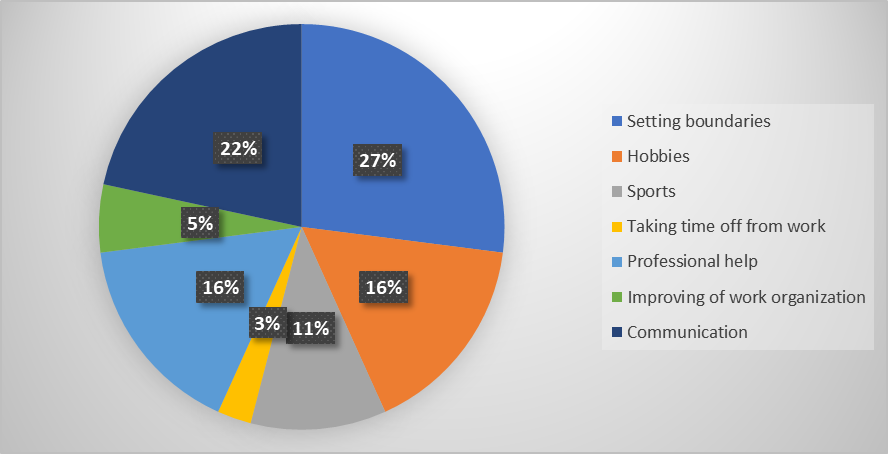
Figure 2. Results of a student survey: «What helps you avoid burnout?»
Constant stress, high workload and work intensity can lead to depletion of physical and psychological resources. Therefore, it is important to know what strategies help activists cope with this challenge (Figure 2).
The majority (27%) of respondents indicated that the ability to avoid burnout is related to the ability to set personal boundaries. This highlights the importance of saying no and setting boundaries between work time and personal life to reduce workload and achieve balance in responsibilities. It is important not to overextend yourself based on your capabilities, and not to overwork if you do not have sufficient physical or psychological resources. About 22% noted communication. This means that regular communication with loved ones, colleagues and like-minded people helps activists regain strength and receive emotional support. The ability to share experiences and discuss work issues reduces stress levels. Hobbies and professional help were chosen by 16% of respondents, respectively. Actively doing what you love, not related to social activities, allows you to distract yourself and restore peace of mind, and receiving professional psychological help in the form of consultations, training or therapy helps to cope with stress and develop self-regulation skills. Some activists (11%) noted that regular physical activity, such as sports, yoga or dance, allows activists to maintain physical and mental health. A small proportion of respondents (5%) noted that improving of work organization, sharing responsibilities, and supporting colleagues also help prevent burnout. The smallest percentage of respondents (3%) indicate that it helps them to temporarily give up work in order to fully recover.
After analyzing the characteristics of the psychology of activists involved in social activities, it becomes obvious that these people play a vital role in the formation of civil society, protecting the rights and interests of citizens, and drawing attention to social problems. Studying the psychology of activists and public figures not only allows us to better understand their motivation and behavior, but also contributes to the development of effective strategies to support this important category of people, which is an important aspect of the development of civil society.
Understanding the psychological characteristics of activists and public figures helps us value and support their contributions to solving social problems. This, in turn, helps to increase social responsibility and the involvement of citizens in public processes.
Thus, the study of the psychology of activists and public figures has important practical significance for increasing the effectiveness of public initiatives and supporting those who guard the interests of society. Further research in this area could make significant contributions to understanding and strengthening civic activism.
References
1. An activist is... the meaning of the word activist: – [Electronic resource]. – Access mode: https://sinonim.org/t/%D0%B0%D0%BA%D1%82%D0%B8%D0%B2%D0%B8%D1%81%D1%822. Stegniy, V. N. Motivation of volunteer activities / V. N. Stegny, M. V. Nikonov // Bulletin of PNIPU. Socio-economic sciences. – 2018. – No. 1. – P. 146-156. – [Electronic resource]. – Access mode: https://vestnik.pstu.ru/soc-eco/archives/?id=&folder_id=7296
3. Znakov, V. V. Understanding in cognition and communication / V. V. Znakov. – Samara: SamSPU, 2010. – 188 p.
4. Schneider, M. I. Empathy as a form of reflection of another person / M. I. Schneider // Humanization of education. – 2016. – No. 2. – P. 60-65. – EDN VZELJJ. – [Electronic resource]. – Access mode: https://elibrary.ru/download/elibrary_26101128_64232308.pdf
5. Tersenov, A. E. Modern youth: motives for engaging in social activities / A. E. Tersenov, T. B. Golubeva // Scientific Review. Pedagogical sciences. – 2020. – No. 1. – P. 54-58. – [Electronic resource]. – Access mode: https://science-pedagogy.ru/ru/article/view?id=2274
6. Balakina, K. Yu. Emotional burnout of volunteers. Causes and prevention / K. Yu. Balakina // Bulletin of Science. – 2023. – No. 11 (68). – Vol. 1. – P. 754-761. – [Electronic resource]. – Access mode: https://www.xn----8sbempclcwd3bmt.xn--p1ai/article/10682
